Remote Spark Jobs on YARN
December 31, 2015
Spark jobs can be run on any cluster managed by Spark’s standalone cluster manager, Mesos, or YARN. In this post, I’m going to discuss submitting remote Spark jobs to YARN. Let’s talk about a non-remote job submission first.
Submit jobs on YARN cluster
Let’s assume you have a YARN cluster set up, and it looks like the following.
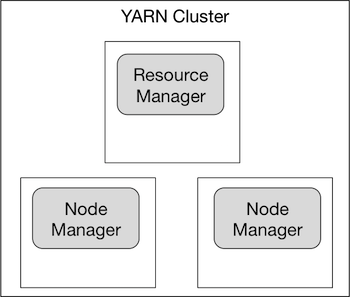
The easy way to run a Spark job is to download the Spark binary directly on one of the nodes in your cluster. You can download a Spark binary and build from source, or you can download a Spark binary pre-built for a Hadoop distribution. If you’re going to do the latter, make sure you download the Spark binary pre-built for the specific version of Hadoop that you are running.
$ ssh -i <your-private-key> <yarn-master-ip>
$ hadoop version # Check the version of hadoop here
$ wget http://d3kbcqa49mib13.cloudfront.net/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6.tgz # Modify for your version
$ tar xvf spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6.tgz
$ cd spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6.tgzThe binary exists on your cluster like this. Note it doesn’t matter which node in the cluster has the binary.
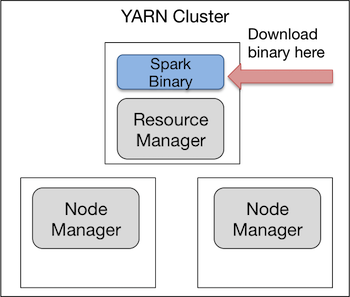
You can run Spark jobs that use YARN as the resource manager directly from that machine:
$ ./bin/spark-submit --master yarn-cluster --class <your-class-entrypoint> app.jar # or --master yarn-client
...
INFO spark.SparkContext: Added JAR file:/home/hduser/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6/lib/spark-examples-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar at http://<resource-manager-ip>/jars/spark-examples-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar with timestamp 1451547756396
WARN metrics.MetricsSystem: Using default name DAGScheduler for source because spark.app.id is not set.
INFO client.RMProxy: Connecting to ResourceManager at <resource-manager-ip>
INFO yarn.Client: Requesting a new application from cluster with 2 NodeManagers
INFO yarn.Client: Verifying our application has not requested more than the maximum memory capability of the cluster (8192 MB per container)
INFO yarn.Client: Will allocate AM container, with 896 MB memory including 384 MB overhead
INFO yarn.Client: Setting up container launch context for our AM
INFO yarn.Client: Setting up the launch environment for our AM container
INFO yarn.Client: Preparing resources for our AM container
INFO yarn.Client: Uploading resource file:/home/hduser/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6/lib/spark-assembly-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar -> hdfs://<resource-manager-ip>/user/hduser/.sparkStaging/application_1447696645162_0133/spark-assembly-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar
What happens? The application code and the Spark assembly JAR are uploaded to HDFS. This assembly JAR contains all the necessary class files for the executors to run Spark. These are the two primary components YARN needs to run your Spark job, and it doesn’t care where the application code or Spark assembly JAR came from. That means we can launch Spark jobs to YARN from machines outside of the cluster, which brings us to remote submission.
Remotely submit jobs to YARN
Submitting a Spark job remotely means executing a Spark job on the YARN cluster but submitting it from a remote machine.
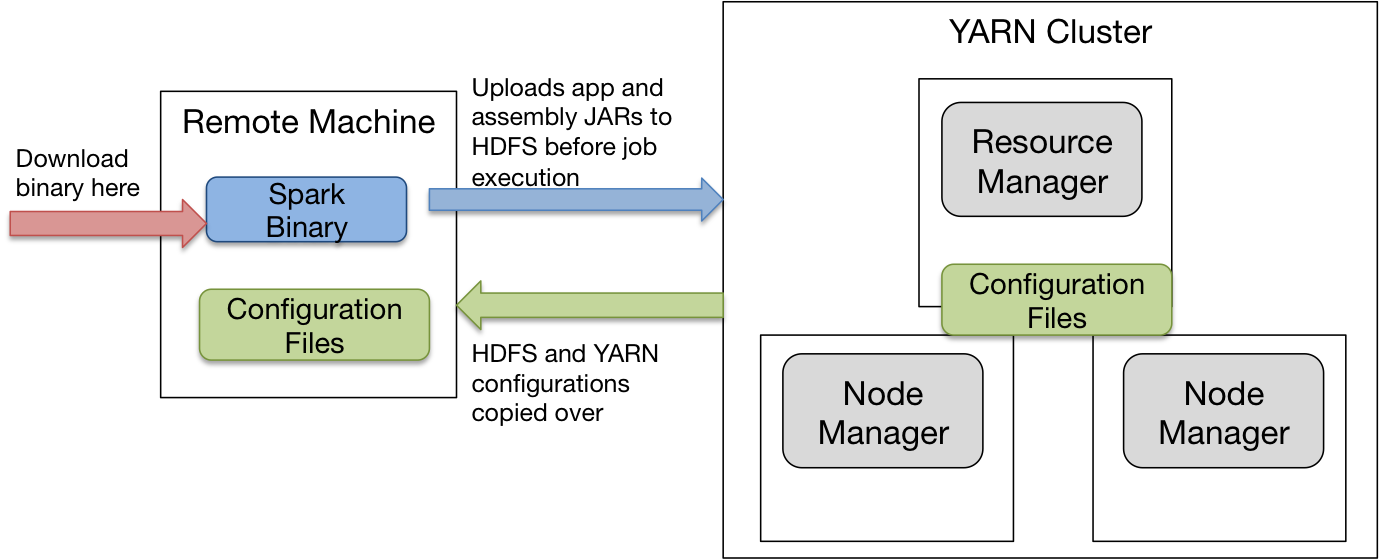
Actually making this work with a Spark standalone cluster is probably more intuitive because you pass in the URL of the Spark master node in spark-submit. But with YARN, you don’t explicitly specify an IP and port. Instead, it pulls the necessary information (such as the IP and port of your resource manager) from the configuration files on your Hadoop cluster. When you submit Spark jobs on your Hadoop cluster, the configuration files are already configured under $HADOOP_CONF_DIR so that’s why it works. For remote submission, we have to copy the files from the Hadoop cluster into the remote machine.
# on yarn cluster
$ ssh -i <your-private-key> <yarn-master-ip>
$ cd $HADOOP_CONF_DIR
$ lsYou’re going to see a lot of files. You only need to copy core-site.xml and yarn-site.xml. Copy these however you like onto your remote machine and set the HADOOP_CONF_DIR environment variable from your remote machine.
# on remote machine
$ export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=<config-files-directory>At this point, you can repeat the steps outlined above to download a Spark binary and execute spark-submit.
# on remote machine
$ wget http://d3kbcqa49mib13.cloudfront.net/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6.tgz # Modify for your hadoop version
$ tar xvf spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6.tgz
$ cd spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6.tgz
$ ./bin/spark-submit --master yarn-cluster --class <your-class-entrypoint> app.jar # or --master yarn-client
...
INFO Client: Requesting a new application from cluster with 2 NodeManagers
15/12/04 00:12:08 INFO Client: Verifying our application has not requested more than the maximum memory capability of the cluster (8192 MB per container)
INFO Client: Will allocate AM container, with 1408 MB memory including 384 MB overhead
INFO Client: Setting up container launch context for our AM
INFO Client: Setting up the launch environment for our AM container
INFO Client: Preparing resources for our AM container
INFO Client: Uploading resource file:/usr/local/spark-1.5.0-bin-hadoop2.6/lib/spark-assembly-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar -> hdfs://<resource-manager-ip>/user/ubuntu/.sparkStaging/application_1447696645162_0137/spark-assembly-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar
INFO Client: Uploading resource file:/api/jars/MyApp.jar -> hdfs://<resource-manager-ip>/user/ubuntu/.sparkStaging/application_1447696645162_0080/MyApp.jar
We’re now submitting jobs remotely! The remote machine is uploading the Spark application code to HDFS and is also connecting to the YARN resource manager. It’s also uploading the Spark assembly JAR to HDFS. We just showed that we can launch Spark jobs from machines outside of the Hadoop cluster.
But you’ll notice that the Spark assembly JAR is uploaded every time you submit a Spark job to YARN. It’s redundant and wastes HDFS disk space if you run lots of Spark jobs using the same distribution of Spark, so let’s optimize this.
# on yarn cluster
$ hdfs dfs -put spark-assembly-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar
$ ./bin/spark-submit --master yarn-cluster --conf spark.yarn.jar=hdfs:///spark-assembly-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar --class <your-class-entrypoint> app.jar
...
INFO Client: Requesting a new application from cluster with 2 NodeManagers
15/12/04 00:12:08 INFO Client: Verifying our application has not requested more than the maximum memory capability of the cluster (8192 MB per container)
INFO Client: Will allocate AM container, with 1408 MB memory including 384 MB overhead
INFO Client: Setting up container launch context for our AM
INFO Client: Setting up the launch environment for our AM container
INFO Client: Preparing resources for our AM container
INFO Client: Source and destination file systems are the same. Not copying hdfs:/spark/spark-assembly-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar
INFO Client: Uploading resource file:/api/jars/MyApp.jar -> hdfs://<resource-manager-ip>/user/ubuntu/.sparkStaging/application_1447696645162_0080/MyApp.jar
You can see in the terminal output that the step to upload the Spark assembly JAR is skipped when running Spark jobs. If you don’t want to specify –conf spark.yarn.jar every time you run spark-submit, you can add this to the configuration for spark defaults.
$ cp conf/spark-defaults.conf.template conf/spark-defaults.conf
$ echo "spark.yarn.jar hdfs:///spark/spark-assembly-1.5.0-hadoop2.6.0.jar" >> conf/spark-defaults.conf